Lake Altaussee has being surveyed using state-of-the-art hydroacoustic measuring methods and investigated hydro-geologically.
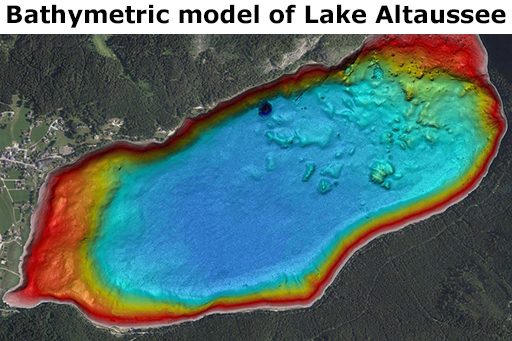
3D Bathymetric Model of the Lake by Multi Beam Echo Sounding (MBES)
With the help of the high-resolution multibeam echo sounder Kongsberg EM-2040, a precise 3D model of the lake basin was created.
It is highly detailed and shows sediment formations, larger rocks, cracks, cables and water supply pipelines at the lake bottom as well as submarine spring pits of varying extent and depth.
Morphology of the Lake bed by MBES Backscatter Analysis
Additionally, backscatter data of the MBES was used to classify zones of different sediments of the lakebed, and to detect objects of interest, such as gas plumes or submarine spring discharges.
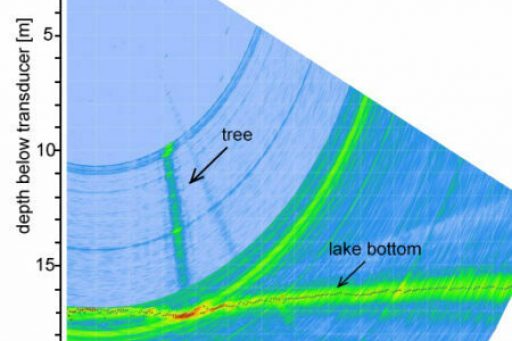
Submerged trees, underwater spring pits and pockmarks by MBES-Watercolumn (WCI)
Furthermore, water column information of the MBES was used to detect objects of interest, such as gas plumes or submarine spring discharges.
Shore and shallow water zones
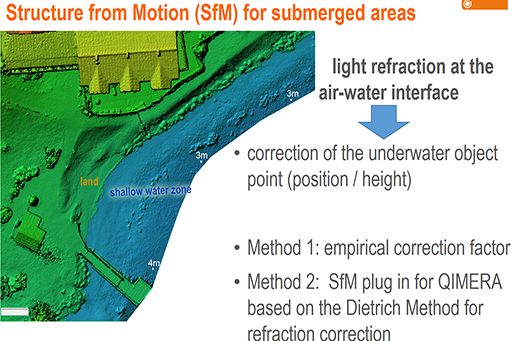
Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) provided high-resolution multi-view stereo imagery from the 5 km long shoreline.
Structure from Motion photogrammetry (SfM) delivered the topographic information of the shallow water zones and its adjacent land zone. Water refraction models were applied to the SfM results to correctly map the lakebed topography of the water-covered areas.
Due to a water transparency value (Secchi depth) of 10 m it was possible to map shallow water zones of up to 2 m water depth.
Thus, a seamless 3D modell of the lake and the surrounding mountains could be produced.
Submerged trees, submarine spring pit and pockmarks – ROV inspection
A remotely operated underwater vehicle (ROV) with a manipulator arm was used to investigate the geological situation of the karst springs located at a depth of 70 m and to map further interesting geomorphological lakebed structures located nearby
Special attention was given to the documentation of submerged trees, which had been identified using watercolumn information from the multibeam echo sounding. This was done by recording video sequences of the entire tree-trunk, its rhizome zone and the surrounding lake bottom.
Contact: Erwin Heine
Department of Civil Engineering
and Natural Hazards (BOKU)








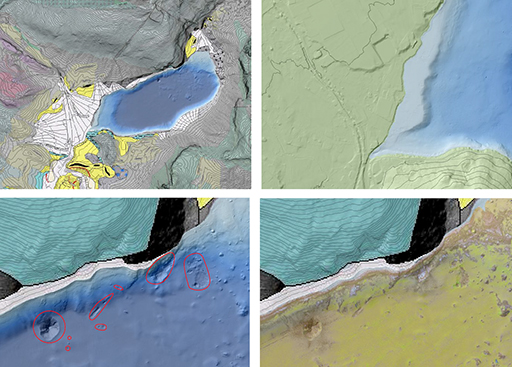
3D Lake Modell for Geomorphological analysis (Wagner, 2021)
